Teach About Biodiversity with Free STEM Lessons & Activities
Use these free STEM lessons and activities to talk about habitats, ecosystems, food webs, and more as you explore biodiversity with K-12 students.

Biodiversity, the "biological diversity" of our planet, is key to human survival. There are an estimated 8.7 million species of plants and animals on Earth, but biodiversity is more than just a count of how many different types of plants and animals (species) exist in an area or on the planet. Biodiversity includes diversity within species (genetic diversity), between species (species diversity), and between ecosystems (ecosystem diversity).
In teaching students about biodiversity, you help students understand biodiversity as a measure of planetary health. With hands-on STEM lessons, students can zoom in and observe markers of biodiversity within individual ecosystems as well as zoom out to see biodiversity as a marker of interconnectedness for the planet as a whole.
The free STEM lessons and activities below help students learn about habitats, ecosystems, biomes, and conditions that can threaten biodiversity, including invasive species, climate change, and human interference. For key terms to review with students, see the list of vocabulary words at the bottom of this resource.
Note: Science Buddies Lesson Plans contain materials to support educators leading hands-on STEM learning with students. Lesson Plans offer NGSS alignment, contain background materials to boost teacher confidence, even in areas that may be new to them, and include supplemental resources like worksheets, videos, discussion questions, and assessment materials. Activities are simplified explorations that can be used in the classroom or in informal learning environments.
Lesson Plans and Activities to Teach About Biodiversity
1. Animal Habitats
In the Animal Habitats lesson, students play a game in which different parts of the classroom represent different habitats. Students will need to figure out what the right habitat is for the animal card they are given as they think about the relationship between habitat and animal survival.

2. Make a Shoebox Habitat
In the Make a Miniature Habitat lesson, students make shoebox habitats from natural materials to mimic the real-life habitat for a chosen animal. As students observe the habitats made by others, they learn that different animals need different resources to survive and not all habitats are suitable for all animals.

3. Make a Bug Collector
In the Explore Biodiversity Using a Homemade Bug Vacuum! activity, students act like wildlife biologists as they use a homemade bug vacuum to find out how many different kinds of bugs and other small invertebrates are in a local habit. By estimating how many species live in a certain area, biologists are able to evaluate the biodiversity and health of an environment. (Tip! For an extended version of this exploration, suitable for a science fair, see the Bug Vacuums: Sucking up Biodiversity project.)

4. How Biodiverse is Your Backyard?
In the How Biodiverse is Your Backyard? activity, students investigate in their own backyard or local natural space to see how many different species of animals they can find and what phyla are represented.

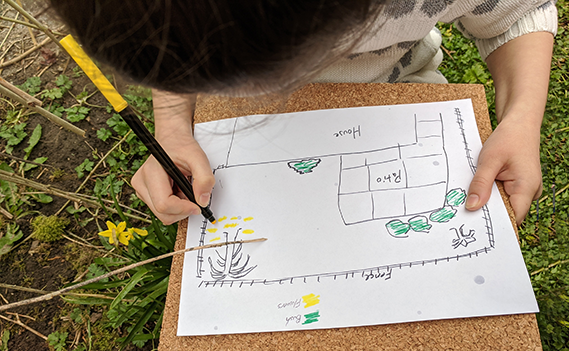
5. Map the Backyard
In the Making Species Maps project, students learn about biogeography and what it means for a species to be cosmopolitan, endemic, invasive, or native. Students then make maps of a local habitat and spend time observing and recording the species they see and determining the type and geographic distribution for the species.
6. A Home for Macroinvertebrates
In the Macroinvertebrate Manor lesson, students build or adapt an existing habitat for macroinvertebrates and then observe to see which organisms survive best in certain conditions and how they adapt to changes in their environment.

"Earthworms!" © 2009 Yun Huang Yong
7. Build a Bird Nest
In the Build a Bird Nest activity, students learn about the many types of nests birds build and why different birds build nests in different locations. Not all birds build nests in trees! As students think about the reasons for these differences, they also build their own model bird nest using natural materials.

8. Build a Bird Feeder
In the Build a Bird Feeder to Study Birds activity, students build their own bird feeder from craft and recycled materials. These feeders can then be used for experiments to see what kinds of birds are in the local area and what types of bird food they prefer.
Tip: For a related discussion about setting up a project to increase the number of birds who come to your backyard, see the Which should you choose? Scientific Method versus Engineering Design Process video.
9. Model World Biomes
In the Home Sweet Biome: How Do Plants Grow in Different Environments? project, students learn about the types of biomes that exist around the world. Students then set up two model terrestrial biomes to investigate the differences in climate and how plants grow in each biome. With recycled plastic bottles, soil, and plant seeds, students simulate and explore differences in plant growth in the temperate forest and the tropical forest. How does a biome differ from a habitat?
(Wikimedia, 2007)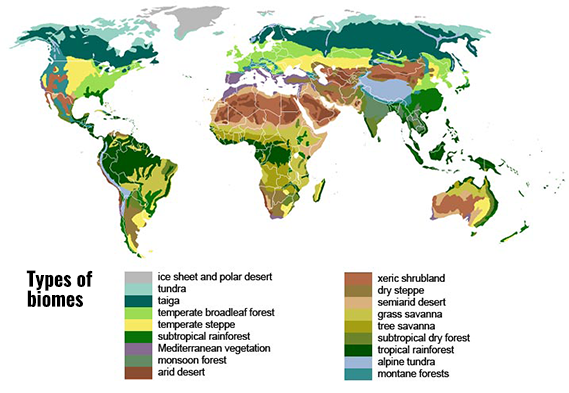
10. Winogradsky Columns
In the Soil Science: Study Microorganisms in Winogradsky Columns activity, students model the Earth's biogeochemical cycle by setting up Winogradsky columns using plastic bottles and mud. They can then investigate how different nutrients relate to which types of soil microorganisms survive.

11. Kelp Forest Food Web
In the How Stable is Your Food Web? lesson, students explore questions related to a food web and its stability by exploring the marine ecosystem of a kelp forest.

"Giant Kelp Forest" © 2010 Tom Thai
12. Discovering Rainforest Locations
In the Discovering Rainforest Locations lesson, students use maps showing worldwide temperature, precipitation, biodiversity, and soil nutrition levels to predict where rainforests are located.
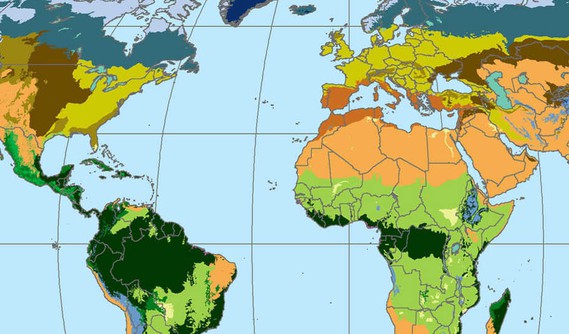
"Global Biomes" © 2012 NASA Socioeconomic Data and Applications Center
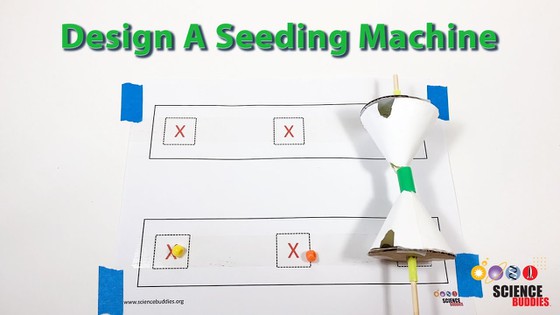
13. Spreading Seeds
In the Design a Seeding Machine to Counteract Deforestation lesson, students learn about deforestation and then use the engineering design process to design a seeding machine to simulate the process of reforestation. This activity challenges students to design and build a seeding machine that can meet specific design requirements, including the need to accurately drop seeds into certain locations on a seeding chart.
14. Microbial Diversity
In the Germ Invasion project, students experiment to see how much microbial diversity exists in their home. With more than 100 million possible types of bacteria, how many will they find in their area, and how can these species be identified and characterized?
15. Modeling an Aquatic Ecosystem
In the From Farms to Phytoplankton lesson, students use a model to see how nutrient pollution from agricultural runoff affects an aquatic ecosystem.

"Morganza Spillway" © 2011 NASA Earth Observatory
Teaching About Biodiversity in K-12
Teaching biodiversity may be a topic in your K-12 classroom as part of an environmental science unit, discussions about sustainability and the future, or lessons about ecosystems, food webs, animals, or the evolutionary history of life on Earth. Understanding biodiversity and how to measure and evaluate biodiversity is important for understanding the health of local areas and our planet as a whole. Many students may initially think biodiversity equates simply to the number of different species in an area. As you teach students more about biodiversity, they learn about several key factors of biodiversity: species diversity, ecosystem diversity, and genetic diversity.
- Species diversity: the number of different species
- Ecosystem diversity: the number of different physical environments (habitats) and the interacting community of organisms that live there
- Genetic diversity: the number of different alleles and traits in a species
In talking with students about biodiversity, many questions for discussion may arise that can lead to engaging classroom discussion and exploration with hands-on STEM learning lessons. What happens to ecological systems and food webs when a species becomes extinct? How are ecosystems related to one another? What role does climate change play in biodiversity? What do genetics have to do with biodiversity and what possibilities or risks might advances in genetic engineering pose?
Note: For additional educator resources to teach about biodiversity, environmental science, and Earth Day, see Earth Day Science Projects and Activities.
Vocabulary
The following word bank contains words that may be covered when teaching about biodiversity using the lessons and activities in this resource.
- Adaptation
- Biodiversity
- Biodiversity loss
- Biogeochemical cycle
- Biogeography
- Biome
- Biosphere
- Carnivore
- Carrying capacity
- Climate change
- Consumer
- Decomposer
- Deforestation
- Diversity index
- Earth's systems
- Ecosystem
- Ecosystem diversity
- Endemic species
- Extinction
- Food chain
- Food web
- Genetic diversity
- Habitat
- Herbivore
- Invasive species
- Mammalian biology
- Native (or indigenous) species
- Omnivore
- Producer
- Reforestation
- Species diversity
- Zoology
Books for Your Shelves
If you and your students are interested in biodiversity, Earth Day, and environmental science, the following Science Buddies books may be a good addition to your classroom or home library shelves!
Projects for Student Exploration
Students interested in nature, environmental science, or other topics related to biodiversity can find related projects in project topic areas at Science Buddies like: Plant Biology, Environmental Science, and Zoology.
These science project and activity roundups may also provide a good starting point for project discovery in an area of interest:
- Bug and Insect STEM Roundup
- 10+ Backyard Bird Science Projects
- Backyard Science: Summer of STEM (Week 10)
Thematic Collections
Collections like this help educators find themed activities in a specific subject area or discover activities and lessons that meet a curriculum need. We hope these collections make it convenient for teachers to browse related lessons and activities. For other collections, see the Teaching Science Units and Thematic Collections lists. We encourage you to browse the complete STEM Activities for Kids and Lesson Plans areas, too. Filters are available to help you narrow your search.
Categories:
You Might Also Enjoy These Related Posts:
- Teach Genetics and Heredity with Free STEM Lessons & Activities - Genetics Science Projects
- 25+ Robotics Projects, Lessons, and Activities
- 15 Density Science Experiments
- Teach Chemical Reactions - 20+ Chemistry Lessons and Activities
- Forces and Laws of Motion Lessons
- Mars Rover Landing: Space Science & Mars STEM Lessons and Activities
- 26 Science Projects and Experiments To Teach About Types of Energy
- 13 Lessons to Teach About the Chemistry of Mixtures and Solutions